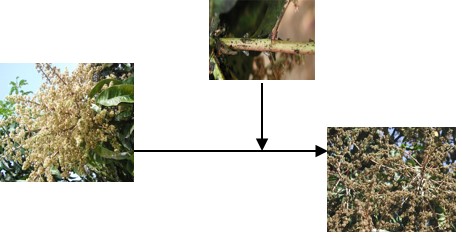
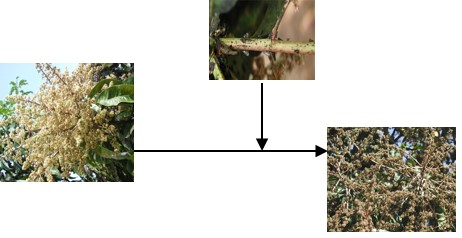
Mango is an important subtropical fruit in India, with high commercial value in internal and export markets. Among the insect pests mango inflorescence hoppers Idioscopus spp at flowering is the most serious.Infestation of the hoppers cause withering of flowers, sooty mold formation due to honey dew secretion resulting up to 100 percent loss in fruit setting and thereby on yield. Presently insecticidal control is recommended for the management of mango hoppers. However, use of chemical insecticides were reported to affect the beneficial organisms such as pollinators that are important for fruit setting.Hence a need to develop alternate safe eco- friendly management strategy such as biological control for the control was attempted by the Institute.
Based on detailed research work carried out for a decade by ICAR-IIHR, Bangalore a biological control strategy by using entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae was developed for management of the pest. An oil based formulation of this fungus was developed by the institute with a prolonged shelf life of more than 12 months that was as effective as chemical pesticides. Two- three sprays of the product at weekly intervals is recommend with recording of hopper infestation on panicles at flowering for effective control of the pest. The product /fungus proved to be safe to pollinators of mango such as Aphis sp, Chryosopha sp etc that are very important for fruit setting in mango.
Information regarding its bio-efficacy, efficacy in different Agro climatic locations, toxicological and eco- toxicological data, shelf life etc are generated for the product.
The formulation was also reported to be effective against many sucking pests especially thrips infesting horticultural crops.
Mango inflorescence hoppers and its impact on mango
Hopper infected byM.anisopliae 

Pollinator of mango 

Updated on 16.02.2017
